一、Linux应用程序基础
Linux应用程序的组成
- 普通的可执行程序文件:一般保存在/usr/bin目录中,普通用户即可执行。
- 服务器程序、管理程序文件:一般保存在/usr/sbin目录中,只有管理员能执行。
- 配置文件:一般保存在/etc目录中,配置文件较多时会建立相应的子目录。
- 日志文件:一般保存在/var/log目录中。
- 关于应用程序的参考文档等数据:一般保存在/usr/share/doc/目录中。
- 执行文件及配置文件的man手册页:一般保存在/usr/share/man/目录中。
二、使用RPM软件包管理工具
1、使用RPM软件包管理命令:rpm
1、查询已安装的RPM软件包信息
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -qa | 显示当前系统中以RPM方式安装的所有软件列表 |
| -qi | 查看指定软件包的名称、版本、许可协议、用途描述等详细信息(--info) |
| -ql | 显示指定的软件包在当前系统中安装的所有目录、文件列表(--list) |
| -qf | 查看指定的文件或目录是由哪个软件包所安装的(--file) |
列出当前操作系统中以RPM方式安装的所有软件包清单
# rpm -qa
查询是否已安装elinks和lynx软件包
# rpm -q elinks lynx
查询系统中是否安装了名称中包含"samba"的软件包,查询时不区分大小写
# rpm -qa | grep -i samba
查询samba-client-libs 软件包的摘要信息
# rpm -qi samba-client-libs
列出wget软件包安装的目录和文件清单
# rpm -ql wget
查询vim编辑器程序是在安装什么软件包时生成
# which vim
/usr/bin/vim
# rpm -qf /usr/bin/vim
vim-enhanced-7.4.629-8.el7_9.x86_64
2、查询RPM软件包文件中的相关信息
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -qpi | 查看指定软件包的名称、版本、许可协议、用途描述等详细信息 |
| -qpl | 查看该软件包准备要安装的所有目标目录、文件列表 |
查询RPM软件包文件kernel-ml-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm的用途
# rpm -qpi kernel-ml-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
warning: kernel-ml-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm: Header V4 DSA/SHA1 Signature, key ID baadae52: NOKEY
Name : kernel-ml
Version : 4.19.12
Release : 1.el7.elrepo
Architecture: x86_64
Install Date: (not installed)
Group : System Environment/Kernel
Size : 215012846
License : GPLv2
Signature : DSA/SHA1, Sat 22 Dec 2018 01:56:27 AM CST, Key ID 309bc305baadae52
Source RPM : kernel-ml-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.src.rpm
Build Date : Sat 22 Dec 2018 01:46:04 AM CST
Build Host : Build64R7
Relocations : (not relocatable)
Packager : Alan Bartlett <ajb@elrepo.org>
Vendor : The ELRepo Project (http://elrepo.org)
URL : https://www.kernel.org/
Summary : The Linux kernel. (The core of any Linux-based operating system.)
Description :
This package provides the Linux kernel (vmlinuz), the core of any
Linux-based operating system. The kernel handles the basic functions
of the OS: memory allocation, process allocation, device I/O, etc.
了解该软件包中包含哪些文件
# rpm -qpl kernel-ml-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
warning: kernel-ml-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm: Header V4 DSA/SHA1 Signature, key ID baadae52: NOKEY
/boot/System.map-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64
/boot/config-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64
/boot/initramfs-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.img
/boot/symvers-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.gz
/boot/vmlinuz-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64
/etc/ld.so.conf.d/kernel-ml-4.19.12-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64.conf
............
2、安装、升级、卸载RPM软件包
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -i | 在当前系统中安装(Install)一个新的RPM软件包 |
| -e | 卸载指定名称的软件包 |
| -U | 检查并升级系统中的某个软件包,若该软件包原来并未安装,则等同于“-i”选项 |
| -F | 检查并更新系统中的某个软件包,若该软件包原来并未安装,则放弃安装 |
| -h | 在安装或升级软件包的过程中,以“#”号显示安装进度 |
| -v | 显示软件安装过程中的详细信息 |
| --force | 强制安装某个软件包,当需要替换已安装的软件包及文件,或者安装一个比当前使用的软件版本更旧的软件时,可以使用此选项 |
| --nodeps | 在安装或升级、卸载一个软件包时,不检查与其他软件包的依赖关系 |
1、安装、升级软件包
全新安装lynx软件包
# rpm -ivh lynx-2.88.8-03.dev15.el7.x86_64.rpm
2、卸载软件包
卸载已安装的 lynx软件
# rpm -e lynx
# rpm -q lynx
package lynx is not installed
3、维护RPM数据库
重建RPM数据库
rpm --rebuilddb
或者
rpm --initdb
导入验证公钥
rpm --import RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
三、搭建YUM仓库服务
1、准备网络安装源(服务器端)
准备软件仓库目录(系统安装光盘)
# mount /dev/cdrom /media/
# mkdir -p /var/ftp/centos7
# cp -rf /media/* /var/ftp/centos7/
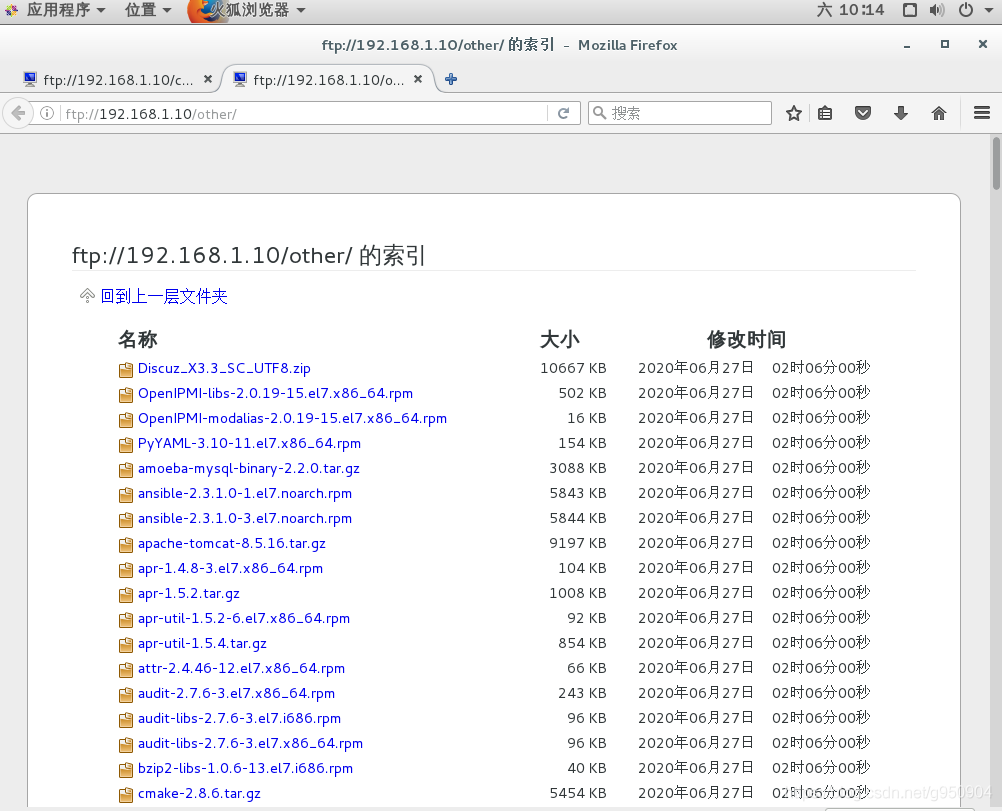
非CentOS 7光盘自带的更多其他软件包(必须包括存在依赖关系的所有安装文件)
# mkdir /var/ftp/other
# cd /var/ftp/other/
# cp -rf /media/* /var/ftp/other/
# createrepo -g /media/repodata/repomd.xml ./ //创建repodata数据文件
安装并启用vsftpd服务
# yum -y install vsftpd
# systemctl start vsftpd
# systemctl enable vsftpd
2、配置软件仓库位置(客户端)
安装ftp客户端
# yum -y install ftp
访问ftp://1 92.168.1.10/centos7/,确保可以查看到已复制到软件仓库目录
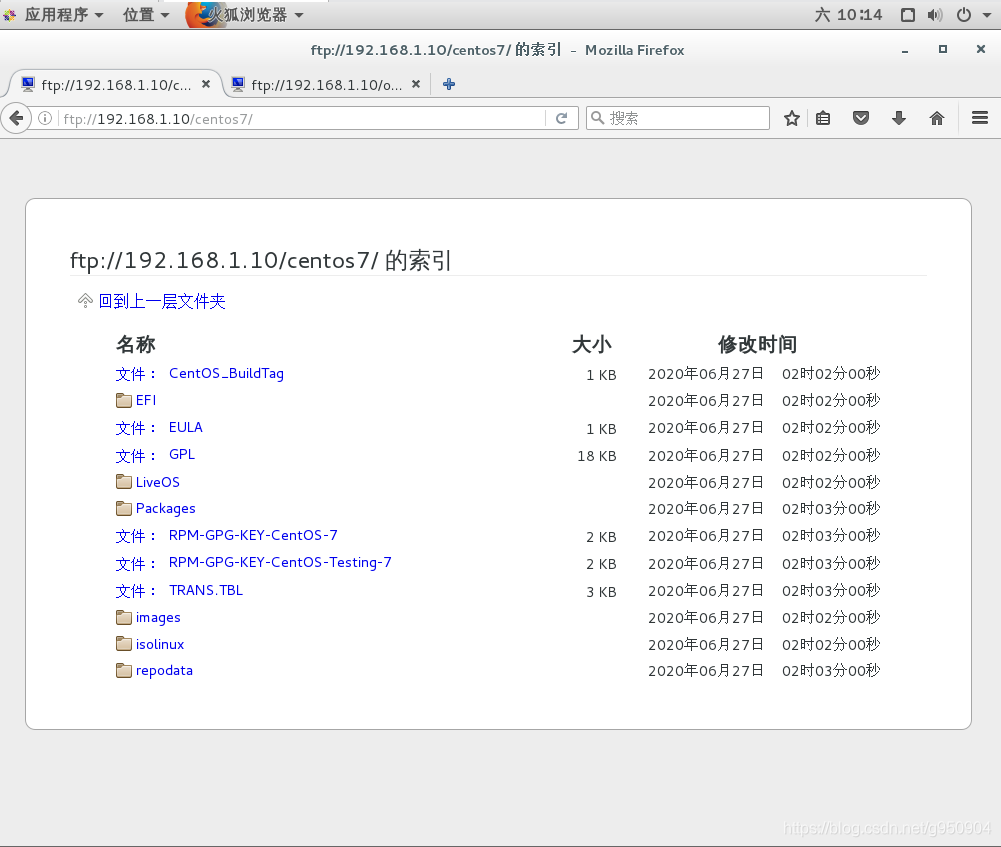
仓库配置
# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
# mkdir backup
# mv *.repo backup/
# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/centos7.repo
[base]
name=centos7
baseurl=ftp://192.168.1.10/centos7
gpgcheck=0
3、使用本地文件夹作为软件仓库
# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/local.repo
[local]
name=local
baseurl=file:///media
gpgcheck=0
四、使用yum工具管理软件包
1、yum 简介
Yum(全称为 Yellow dog Updater, Modified)是一个在Fedora和RedHat以及CentOS中的包管理器。基于RPM包管理,能够从指定的服务器自动下载RPM包并且安装,可以自动处理依赖性关系,并且一次安装所有依赖的软件包,无须繁琐地一次次下载、安装。
Yum的关键之处是要有可靠的repository,顾名思义这就是软件的仓库,它可以是http或者ftp站点,也可以是本地的软件池,但是必须包含rpm的header,rmp的header包括了rmp的各种信息,包括描述、功能、提供的文件、依赖性等,正是收集了这些信息,才能自动化的完成余下的任务。
repo文件是yum源(软件仓库)的配置文件,通常一个repo文件定义了一个或者多个软件仓库的细节内容
RPM包的名称规则示例:ttpd-manual- 2.0.40-21.i386.rpm,ttp-manual是软件包的名称,2是主版本号;0是次版本号;40是修正号;21是编译的次数;i386是适合的平台
2、YUM命令详解
yum的命令形式一般是如下:yum [选项] [参数] [package ...]
选项
-h, --help 显示此帮助消息并退出
-t, --tolerant 忽略错误
-C, --cacheonly 完全从系统缓存运行,不升级缓存
-c [config file], --config=[config file] 配置文件路径
-R [minutes], --randomwait=[minutes] 命令最长等待时间
-d [debug level], --debuglevel=[debug level] 调试输出级别
--showduplicates 在 list/search 命令下,显示源里重复的条目
-e [error level], --errorlevel=[error level] 错误输出级别
--rpmverbosity=[debug level name] RPM 调试输出级别
-q, --quiet 静默执行
-v, --verbose 详尽的操作过程
-y, --assumeyes 回答全部问题为是
--assumeno 回答全部问题为否
--version 显示 Yum 版本然后退出
--installroot=[path] 设置安装根目录
--enablerepo=[repo] 启用一个或多个软件源(支持通配符)
--disablerepo=[repo] 禁用一个或多个软件源(支持通配符)
-x [package], --exclude=[package] 采用全名或通配符排除软件包
--disableexcludes=[repo] 禁止从主配置,从源或者从任何位置排除
--disableincludes=[repo] disable includepkgs for a repo or for everything
--obsoletes 更新时处理软件包取代关系
--noplugins 禁用 Yum 插件
--nogpgcheck 禁用 GPG 签名检查
--disableplugin=[plugin] 禁用指定名称的插件
--enableplugin=[plugin] 启用指定名称的插件
--skip-broken 忽略存在依赖关系问题的软件包
--color=COLOR 配置是否使用颜色
--releasever=RELEASEVER 在 yum 配置和 repo 文件里设置 $releasever 的值
--downloadonly 仅下载而不更新
--downloaddir=DLDIR 指定一个其他文件夹用于保存软件包
--setopt=SETOPTS 设置任意配置和源选项
--bugfix Include bugfix relevant packages, in updates
--security Include security relevant packages, in updates
--advisory=ADVS, --advisories=ADVS Include packages needed to fix the given advisory, in updates
--bzs=BZS Include packages needed to fix the given BZ, in updates
--cves=CVES Include packages needed to fix the given CVE, in updates
--sec-severity=SEVS, --secseverity=SEVS Include security relevant packages matching the severity, in updates
参数
check 检查 RPM 数据库问题
check-update 检查是否有可用的软件包更新
clean 删除缓存数据
deplist 列出软件包的依赖关系
distribution-synchronization 已同步软件包到最新可用版本
downgrade 降级软件包
erase 从系统中移除一个或多个软件包
fs Acts on the filesystem data of the host, mainly for removing docs/lanuages for minimal hosts.
fssnapshot Creates filesystem snapshots, or lists/deletes current snapshots.
groups 显示或使用、组信息
help 显示用法提示
history 显示或使用事务历史
info 显示关于软件包或组的详细信息
install 向系统中安装一个或多个软件包
langavailable Check available languages
langinfo List languages information
langinstall Install appropriate language packs for a language
langlist List installed languages
langremove Remove installed language packs for a language
list 列出一个或一组软件包
load-transaction 从文件名中加载一个已存事务
makecache 创建元数据缓存
provides 查找提供指定内容的软件包
reinstall 覆盖安装软件包
repo-pkgs 将一个源当作一个软件包组,这样我们就可以一次性安装/移除全部软件包。
repolist 显示已配置的源
search 在软件包详细信息中搜索指定字符串
shell 运行交互式的 yum shell
swap Simple way to swap packages, instead of using shell
update 更新系统中的一个或多个软件包
update-minimal Works like upgrade, but goes to the 'newest' package match which fixes a problem that affects your system
updateinfo Acts on repository update information
upgrade 更新软件包同时考虑软件包取代关系
version 显示机器和/或可用的源版本。
3、常用命令
1、查询软件包
# yum list //查看获得系统中的软件安装情况
# yum list installed //只列出系统中已安装的软件包
# yum list available //只列出软件仓库中可用(尚未安装)的软件包
# yum list updates //只列出可以升级版本的软件包
2、yum info:查询软件包的描述信息
# yum info vsftpd
3、yum search:查询指定的软件包
# yum search all httpd
4、安装、升级、卸载软件包
下载并安装net-snmp软件包,并自动解决其依赖关系
# yum -y install net-snmp
卸载autofs软件包,并自动解决其依赖关系
# yum -y remove autofs
软件升级
yum update
yum upgrade
yum update与yum upgrade的区别
- yum update 只更新软件,不更新内核
- yum upgrade 升级所有包,不改变软件设置和系统设置,系统版本升级,内核不改变
5、修改源的配置文件
repo文件
[serverid]
#serverid是用于区别各个不同的repository,必须有一个独一无二的名称。若重复了,是前面覆盖后面--还是反过来呢???用enabled 测试是后面覆盖前面
name=Some name for this server
#name,是对repository的描述,支持像$releasever $basearch这样的变量; name=Fedora Core $releasever - $basearch - Released Updates
baseurl=url://path/to/repository/
# 1. 格式: baseurl=url://server1/path/to/repository/, url支持的协议有 http:// ftp:// file://三种。
# 2. baseurl后可以跟多个url,你可以自己改为速度比较快的镜像站,但#baseurl只能有一个
# 3. 其中url指向的目录必须是这个repository header目录的上一级,它也支持$releasever $basearch这样的变量。
gpgcheck=1
exclude=gaim
failovermethod=priority
#failovermethode有两个选项roundrobin和priority,意思分别是有多个url可供选择时,yum选择的次序,roundrobin是随机选择,如果连接失 败则使用下一个,依次循环,priority则根据url的次序从第一个开始。如果不指明,默认是roundrobin。
enabled=[1 or 0]
# 1. 当某个软件仓库被配置成 enabled=0 时,yum 在安装或升级软件包时不会将该仓库做为软件包提供源。使用这个选项,可以启用或禁用软件仓库。
# 2. 通过 yum 的 --enablerepo=[repo_name] 和 --disablerepo=[repo_name] 选项,或者通过 PackageKit 的"添加/删除软件"工具,也能够方便地启用和禁用指定的软件仓库
变量解释:
# $releasever 发行版的版本,从[main]部分的distroverpkg获取,如果没有,则根据redhat-release包进行判断。
# $arch cpu体系,如i686,athlon等
# $basearch cpu的基本体系组,如i686和athlon同属i386,alpha和alphaev6同属alpha。
修改源的配置文件 /etc/yum.repos.d/ ,将默认的一个文件做成一个备份,然后自己新建以 .repo 结尾的文件,用vim编辑器打开
# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
# pwd
/etc/yum.repos.d
# mkdir backup
# mv *.repo backup/
1、配置本地源
# vim my.repo
[myrepo] //仓库源名称
name=NewRepo //对yum的描述
baseurl=file:///media //baseurl表示声明yum可以管理并使用的rpm包路径,
enable=1 //表示当前仓库是否开启,1为开启,0为关闭,此项不写默认为开启
gpgcheck=0 //gpgcheck表示安装rpm包时,是否基于公私钥对匹配包的安全信息,1表示开启,0表示关闭,此项不写默认为验证
# yum clean all //清理yum缓存
# yum repolist //启用仓库
2、配置网络源
下载国内阿里的yum源
# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
# yum repolist
国内其他yum源的地址
网易163yum源,安装方法查看:http://mirrors.163.com/
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.backup
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.163.com/.help/CentOS7-Base-163.repo
yum clean all
yum makecache
高校的 yum源,安装方法查看:https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/help/centos.html
sudo sed -e 's|^mirrorlist=|#mirrorlist=|g' \
-e 's|^#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos|baseurl=https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos|g' \
-i.bak \
/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
yum makecache
腾讯的 yum源,安装方法查看:https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.backup
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/repo/centos7_base.repo
yum clean all
yum makecache
3、拓展yum源
EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux)是基于Fedora的一个项目,为“红帽系”的操作系统提供额外的软件包,适用于RHEL、CentOS和Scientific Linux。
阿里yum扩展源
# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
# yum repolist
# yum makecache fast
高校的 yum扩展源
sudo yum install -y epel-release
sudo sed -e 's|^metalink=|#metalink=|g' \
-e 's|^#baseurl=https\?://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/|baseurl=https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/epel/|g' \
-i.bak \
/etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo
腾讯的 yum扩展源
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo.backup
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/repo/epel-7.repo
yum clean all
yum makecache
五、离线yum源
1、开启yum缓存功能
将要下载的软件下载到拥有网络的主机,软件包会自动缓存到本机
# vi /etc/yum.conf
[main]
cachedir=/var/cache/yum/$basearch/$releasever #这是存放rmp文件的路径
keepcache=1 #如果是0,则不保存,如果是1则保存,我们这里修改为1
debuglevel=2
logfile=/var/log/yum.log
exactarch=1
obsoletes=1
gpgcheck=1
plugins=1
installonly_limit=5
bugtracker_url=http://bugs.centos.org/set_project.php?project_id=23&ref=http://bugs.centos.org/bug_report_page.php?category=yum
distroverpkg=centos-release
2、Createrepo创建本地YUM镜像源
- 将CentOS版本系统镜像中的Packages并上传到主机上的某一目录下
- 安装createrepo用来创建软件包的索引。或者将系统镜像中repodata目录放到rpm包路径下
# yum -y install createrepo
Createrepo命令参数详解
-u --baseurl <url> 指定Base URL的地址
-o --outputdir <url> 指定元数据的输出位置
-x --excludes <packages> 指定在形成元数据时需要排除的包
-i --pkglist <filename> 指定一个文件,该文件内的包信息将被包含在即将生成的元数据中,格式为每个包信息独占一行,不含通配符、正则,以及范围表达式。
-n --includepkg 通过命令行指定要纳入本地库中的包信息,需要提供URL或本地路径。
-q --quiet 安静模式执行操作,不输出任何信息。
-g --groupfile <groupfile> 指定本地软件仓库的组划分,范例如下:createrepo -g comps.xml /path/to/rpms注意:组文件需要和rpm包放置于同一路径下。
-v --verbose 输出详细信息。
-c --cachedir <path> 指定一个目录,用作存放软件仓库中软件包的校验和信息。
当createrepo在未发生明显改变的相同仓库文件上持续多次运行时,指定cachedir会明显提高 其性能。
--update 如果元数据已经存在,且软件仓库中只有部分软件发生了改变或增减,
则可用update参数直接对原有元数据进行升级,效率比重新分析rpm包依赖并生成新的元数据要 高很多。
-p --pretty 以整洁的格式输出xml文件。
-d --database 该选项指定使用SQLite来存储生成的元数据,默认项。
创建索引文件夹
# mkdir -p /package/yumsource
# createrepo /package/yumsource
local.repo
baseurl=file:///package/yumsource
六、Reposync同步YUM远程仓库的安装包
1、安装
yum install yum-utils -y
2、命令参数
Usage:
Reposync is used to synchronize a remote yum repository to a local
directory using yum to retrieve the packages.
/usr/bin/reposync [options]
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-c CONFIG, --config=CONFIG config file to use (defaults to /etc/yum.conf)
-a ARCH, --arch=ARCH act as if running the specified arch (default: current arch, note: does not override $releasever. x86_64 is a superset for i*86.)
--source operate on source packages
-r REPOID, --repoid=REPOID secify repo ids to query, can be specified multiple times (default is all enabled)
-e CACHEDIR, --cachedir=CACHEDIR directory in which to store metadata
-t, --tempcache Use a temp dir for storing/accessing yum-cache
-d, --delete delete local packages no longer present in repository
-p DESTDIR, --download_path=DESTDIR Path to download packages to: defaults to current dir
--norepopath Don't add the reponame to the download path. Can only be used when syncing a single repository (default is to add the reponame)
-g, --gpgcheck Remove packages that fail GPG signature checking after downloading
-u, --urls Just list urls of what would be downloaded, don't download
-n, --newest-only Download only newest packages per-repo
-q, --quiet Output as little as possible
-l, --plugins enable yum plugin support
-m, --downloadcomps also download comps.xml
--download-metadata download all the non-default metadata
3、示例
$> bash -c 'cat > ceph.repo <<EOF
[Ceph]
name=Ceph packages for \$basearch
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/rpm-jewel/el7/\$basearch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
type=rpm-md
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc
priority=1
[Ceph-noarch]
name=Ceph noarch packages
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/rpm-jewel/el7/noarch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
type=rpm-md
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc
priority=1
EOF' ;\
reposync --repoid=Ceph-noarch -p /data/ -n -c ceph.repo
# --repoid指定的是RepoID
# -p指定的是存储的目录
# -n指定下载最新的包
# -c指定的是repo文件的路径,默认的是/etc/yum.repo.d目录下的repo文件
七、下载软件RPM包以及其依赖包
1、yum插件yumdownloadonly
downloadonly可以仅下载所需软件和及其依赖包
# yum install yum-plugin-downloadonly
# yum install --downloadonly +软件名称 --downloaddir=指定rpm包存放路径
2、使用yum-utils的命令yumdownloader
单纯的使用yumdownloader 只会下载给定名称的既定RPM包,安装时候所需要的一些依赖不会被下载。如果要下载依赖加上"--resolve"参数,如果要指定下载目录。加上"--destdir"参数
# yum install -y yum-utils
# yumdownloader --resolve +软件名称 --destdir=指定rpm包依赖存放路径


评论区